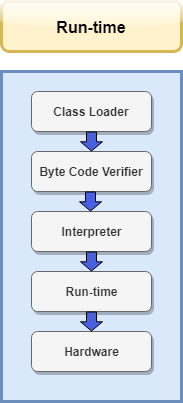
1. Into hdfs by using sqoop
2. Into hive by using sqoop
$ sqoop list-databases --connect jdbc:mysql://localhost/world --username root -P
$ sqoop eval --connect jdbc:mysql://localhost/world --username root -P --query "SELECT * FROM city LIMIT 10"
$ sqoop import --connect jdbc:mysql://localhost/world --table city -m1 --username root -P
sqoop import --connect jdbc:mysql://localhost/world --table city --username root -P
$ sqoop import --connect jdbc:mysql://localhost/world --table city --username root -P --target-dir /user/cloudera/world_city/ -m1
$ sqoop import-all-tables --connect jdbc:mysql://localhost/world -m1 --warehouse-dir /user/cloudera/world_city1/ --username root -P
• sqoop import --connect jdbc:mysql://localhost/world --table city --username root -P --split-by ID --target-dir /user/cloudera/lab2
cloudera@localhost> $sqoop export --connect jdbc:mysql://localhost/employee --table emp -m1 --export-dir/user/cloudera/emp --input --fields --terminated-by ‘,’
$sqoop job --create importtoday -- import --connect jdbc:mysql://localhost/world --table city -m1 --username root -P
$ sqoop import --connect jdbc:mysql://localhost/world --table city -m1 --username root -P --hive-import
1. Import data from a table in a relational database into HDFS
2. Import the results of a query from a relational data bases into HDFS
3. Import a table from relational database into a new or existing Hive
4. Insert or update data from HDFS into a table in a relational
1. Import data from a table in a relational database into HDFS
2. Import the results of a query from a relational data bases into HDFS
3. Import a table from relational database into a new or existing Hive
4. Insert or update data from HDFS into a table in a relational
---------------------------***practice makes perfect *** do more practice***------------------
sqoop list-databases \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://localhost/world" \
--username root \
--password cloudera
sqoop list-tables --connect "jdbc:mysql://localhost/world" \
--username root \
--password cloudera
sqoop eval \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://localhost/world" \
--username root \
--password cloudera \
--query "select count(1) from City"
sqoop import \
-m 12 \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://localhost/world" \
--username root \
--password cloudera \
--table City
--as-avrodatafile \
--warehouse-dir=/user/hive/warehouse/retail_stage.db
--Default
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://localhost/world" \
--username root \
--password cloudera \
--table City \
--as-textfile \
--target-dir=/user/cloudera/departments
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://localhost/world" \
--username root \
--password cloudera \
--table City \
--as-sequencefile \
--target-dir=/user/cloudera/City
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://localhost/world" \
--username root \
--password cloudera \
--table City \
--as-avrodatafile \
--target-dir=/user/cloudera/departments
-- A file with extension avsc will be created under the directory from which sqoop import is executed
-- Copy avsc file to HDFS location
-- Create hive table with LOCATION to /user/cloudera/departments and TBLPROPERTIES pointing to avsc file
hadoop fs -put sqoop_import_departments.avsc /user/cloudera
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE departments
ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.avro.AvroSerDe'
STORED AS INPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.avro.AvroContainerInputFormat'
OUTPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.avro.AvroContainerOutputFormat'
LOCATION 'hdfs:///user/cloudera/departments'
TBLPROPERTIES ('avro.schema.url'='hdfs://quickstart.cloudera/user/cloudera/sqoop_import_departments.avsc');
-- It will create tables in default database in hive
-- Using snappy compression
-- As we have imported all tables before make sure you drop the directories
-- Launch hive drop all tables
drop table departments;
drop table categories;
drop table products;
drop table orders;
drop table order_items;
drop table customers;
-- Dropping directories, in case your hive database/tables in consistent state
hadoop fs -rm -R /user/hive/warehouse/departments
hadoop fs -rm -R /user/hive/warehouse/categories
hadoop fs -rm -R /user/hive/warehouse/products
hadoop fs -rm -R /user/hive/warehouse/orders
hadoop fs -rm -R /user/hive/warehouse/order_itmes
hadoop fs -rm -R /user/hive/warehouse/customers
sqoop import-all-tables \
--num-mappers 1 \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://localhost/world" \
--username=root \
--password=cloudera \
--hive-import \
--hive-overwrite \
--create-hive-table \
--compress \
--compression-codec org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.SnappyCodec \
--outdir java_files
sudo -u hdfs hadoop fs -mkdir /user/cloudera/retail_stage
sudo -u hdfs hadoop fs -chmod +rw /user/cloudera/retail_stage
hadoop fs -copyFromLocal ~/*.avsc /user/cloudera/retail_stage
-- Basic import
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username=retail_dba \
--password=cloudera \
--table departments \
--target-dir /user/cloudera/departments
-- Boundary Query and columns
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username=retail_dba \
--password=cloudera \
--table departments \
--target-dir /user/cloudera/departments \
-m 2 \
--boundary-query "select 2, 8 from departments limit 1" \
--columns department_id,department_name
-- query and split-by
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username=retail_dba \
--password=cloudera \
--query="select * from orders join order_items on orders.order_id = order_items.order_item_order_id where \$CONDITIONS" \
--target-dir /user/cloudera/order_join \
--split-by order_id \
--num-mappers 4
-- Copying into existing table or directory (append)
-- Customizing number of threads (num-mappers)
-- Changing delimiter
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username=retail_dba \
--password=cloudera \
--table departments \
--target-dir /user/hive/warehouse/retail_ods.db/departments \
--append \
--fields-terminated-by '|' \
--lines-terminated-by '\n' \
--num-mappers 1 \
--outdir java_files
-- Importing table with out primary key using multiple threads (split-by)
-- When using split-by, using indexed column is highly desired
-- If the column is not indexed then performance will be bad
-- because of full table scan by each of the thread
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username=retail_dba \
--password=cloudera \
--table departments \
--target-dir /user/hive/warehouse/retail_ods.db/departments \
--append \
--fields-terminated-by '|' \
--lines-terminated-by '\n' \
--split-by department_id \
--outdir java_files
-- Getting delta (--where)
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username=retail_dba \
--password=cloudera \
--table departments \
--target-dir /user/hive/warehouse/retail_ods.db/departments \
--append \
--fields-terminated-by '|' \
--lines-terminated-by '\n' \
--split-by department_id \
--where "department_id > 7" \
--outdir java_files
-- Incremental load
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username=retail_dba \
--password=cloudera \
--table departments \
--target-dir /user/hive/warehouse/retail_ods.db/departments \
--append \
--fields-terminated-by '|' \
--lines-terminated-by '\n' \
--check-column "department_id" \
--incremental append \
--last-value 7 \
--outdir java_files
sqoop job --create sqoop_job \
-- import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username=retail_dba \
--password=cloudera \
--table departments \
--target-dir /user/hive/warehouse/retail_ods.db/departments \
--append \
--fields-terminated-by '|' \
--lines-terminated-by '\n' \
--check-column "department_id" \
--incremental append \
--last-value 7 \
--outdir java_files
sqoop job --list
sqoop job --show sqoop_job
sqoop job --exec sqoop_job
-- Hive related
-- Overwrite existing data associated with hive table (hive-overwrite)
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username=retail_dba \
--password=cloudera \
--table departments \
--fields-terminated-by '|' \
--lines-terminated-by '\n' \
--hive-home /user/hive/warehouse/retail_ods.db \
--hive-import \
--hive-overwrite \
--hive-table departments \
--outdir java_files
--Create hive table example
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username=retail_dba \
--password=cloudera \
--table departments \
--fields-terminated-by '|' \
--lines-terminated-by '\n' \
--hive-home /user/hive/warehouse \
--hive-import \
--hive-table departments_test \
--create-hive-table \
--outdir java_files
--Connect to mysql and create database for reporting database
--user:root, password:cloudera
mysql -u root -p
create database retail_rpt_db;
grant all on retail_rpt_db.* to retail_dba;
flush privileges;
use retail_rpt_db;
create table departments as select * from retail_db.departments where 1=2;
exit;
--For certification change database name retail_rpt_db to retail_db
sqoop export --connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_rpt_db" \
--username retail_dba \
--password cloudera \
--table departments \
--export-dir /user/hive/warehouse/retail_ods.db/departments \
--input-fields-terminated-by '|' \
--input-lines-terminated-by '\n' \
--num-mappers 2 \
--batch \
--outdir java_files
sqoop export --connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username retail_dba \
--password cloudera \
--table departments \
--export-dir /user/cloudera/sqoop_import/departments_export \
--batch \
--outdir java_files \
-m 1 \
--update-key department_id \
--update-mode allowinsert
sqoop export --connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username retail_dba \
--password cloudera \
--table departments_test \
--export-dir /user/hive/warehouse/departments_test \
--input-fields-terminated-by '\001' \
--input-lines-terminated-by '\n' \
--num-mappers 2 \
--batch \
--outdir java_files \
--input-null-string nvl \
--input-null-non-string -1
--Merge process begins
hadoop fs -mkdir /user/cloudera/sqoop_merge
--Initial load
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username=retail_dba \
--password=cloudera \
--table departments \
--as-textfile \
--target-dir=/user/cloudera/sqoop_merge/departments
--Validate
sqoop eval --connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username retail_dba \
--password cloudera \
--query "select * from departments"
hadoop fs -cat /user/cloudera/sqoop_merge/departments/part*
--update
sqoop eval --connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username retail_dba \
--password cloudera \
--query "update departments set department_name='Testing Merge' where department_id = 9000"
--Insert
sqoop eval --connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username retail_dba \
--password cloudera \
--query "insert into departments values (10000, 'Inserting for merge')"
sqoop eval --connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username retail_dba \
--password cloudera \
--query "select * from departments"
--New load
sqoop import \
--connect "jdbc:mysql://quickstart.cloudera:3306/retail_db" \
--username=retail_dba \
--password=cloudera \
--table departments \
--as-textfile \
--target-dir=/user/cloudera/sqoop_merge/departments_delta \
--where "department_id >= 9000"
hadoop fs -cat /user/cloudera/sqoop_merge/departments_delta/part*
--Merge
sqoop merge --merge-key department_id \
--new-data /user/cloudera/sqoop_merge/departments_delta \
--onto /user/cloudera/sqoop_merge/departments \
--target-dir /user/cloudera/sqoop_merge/departments_stage \
--class-name departments \
--jar-file
hadoop fs -cat /user/cloudera/sqoop_merge/departments_stage/part*
--Delete old directory
hadoop fs -rm -R /user/cloudera/sqoop_merge/departments
--Move/rename stage directory to original directory
hadoop fs -mv /user/cloudera/sqoop_merge/departments_stage /user/cloudera/sqoop_merge/departments
--Validate that original directory have merged data
hadoop fs -cat /user/cloudera/sqoop_merge/departments/part*
--Merge process ends
sqoop import --connect "jdbc:mysql://localhost/world" --username=root --password=cloudera --query="select City.*,CountryLanguage.Percentage,CountryLanguage.IsOfficial from City join CountryLanguage on City.CountryCode = CountryLanguage.CountryCode where City.ID=4079 and \$CONDITIONS" --target-dir /user/cloudera/order_join -m 1